Summary report
For computational reproducibility assessment of Allen et al. 2020
Study
Allen, M., Bhanji, A., Willemsen, J., Dudfield, S., Logan, S., & Monks, T. A simulation modelling toolkit for organising outpatient dialysis services during the COVID-19 pandemic. PLoS One 15, 8 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0237628.
This is a discrete-event simulation modeling patient allocation to dialysis units during the pandemic. The patients need to be transported to a dialysis unit several times a week but, during the pandemic, it was required that COVID positive patients were kept seperate from COVID negative patients. The proposed plan was that all COVID negative units were sent to a particular unit (with a second overflow unit). This study tests that plan with a worst-case scenario of COVID spread over 150 days.
Computational reproducibility
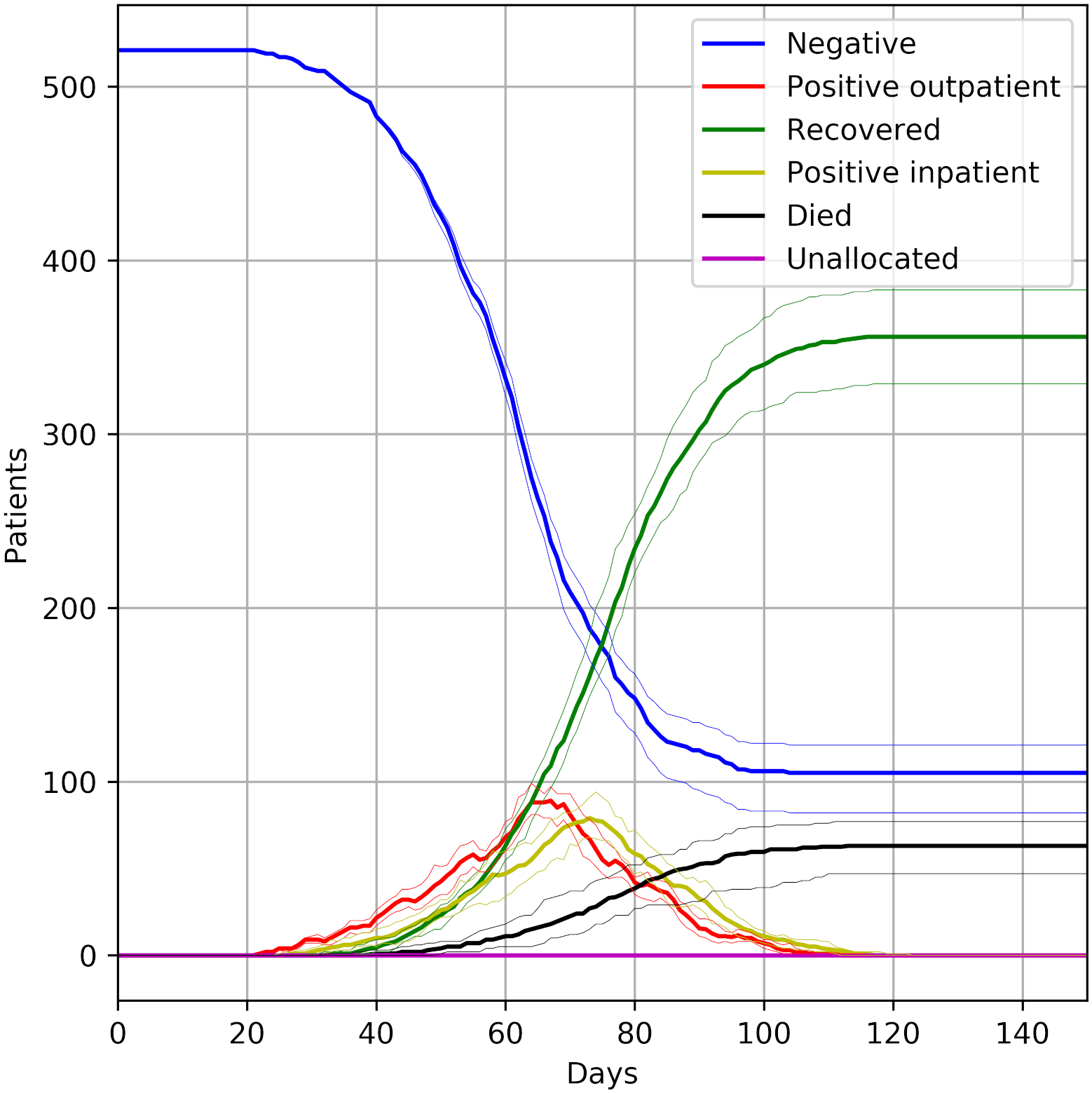
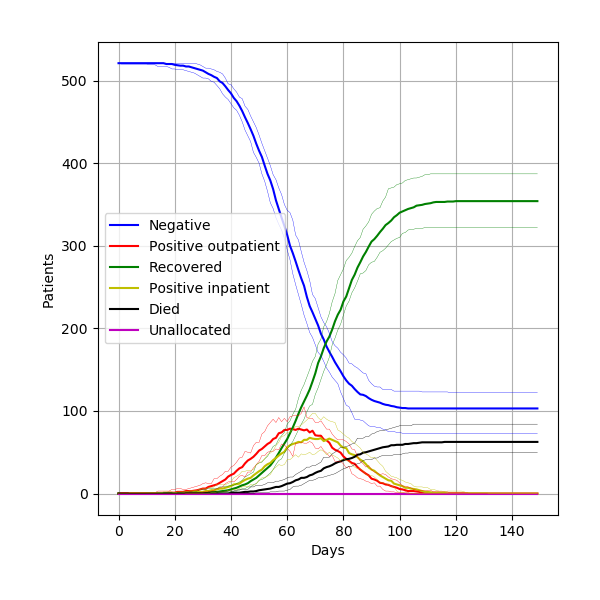
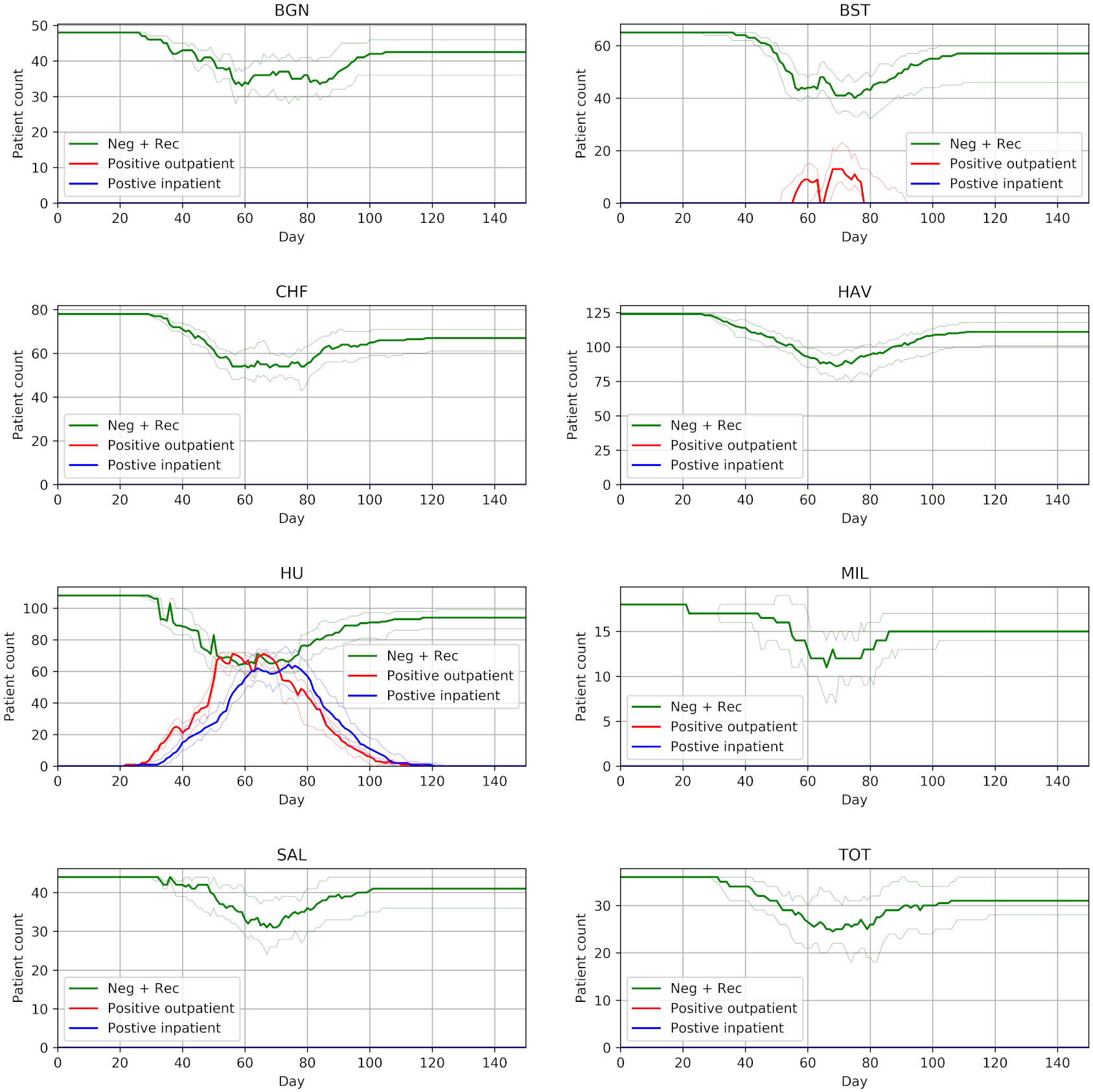
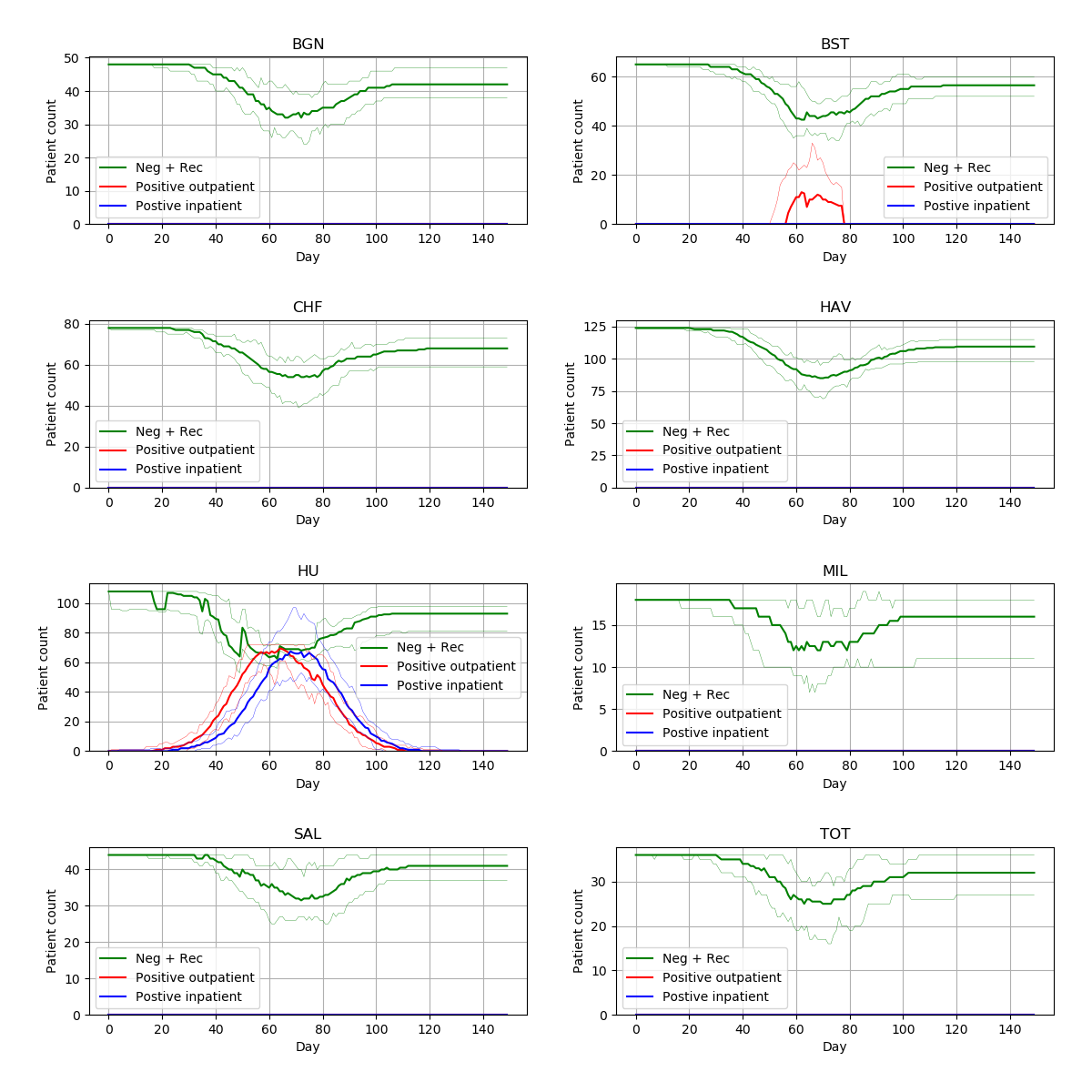
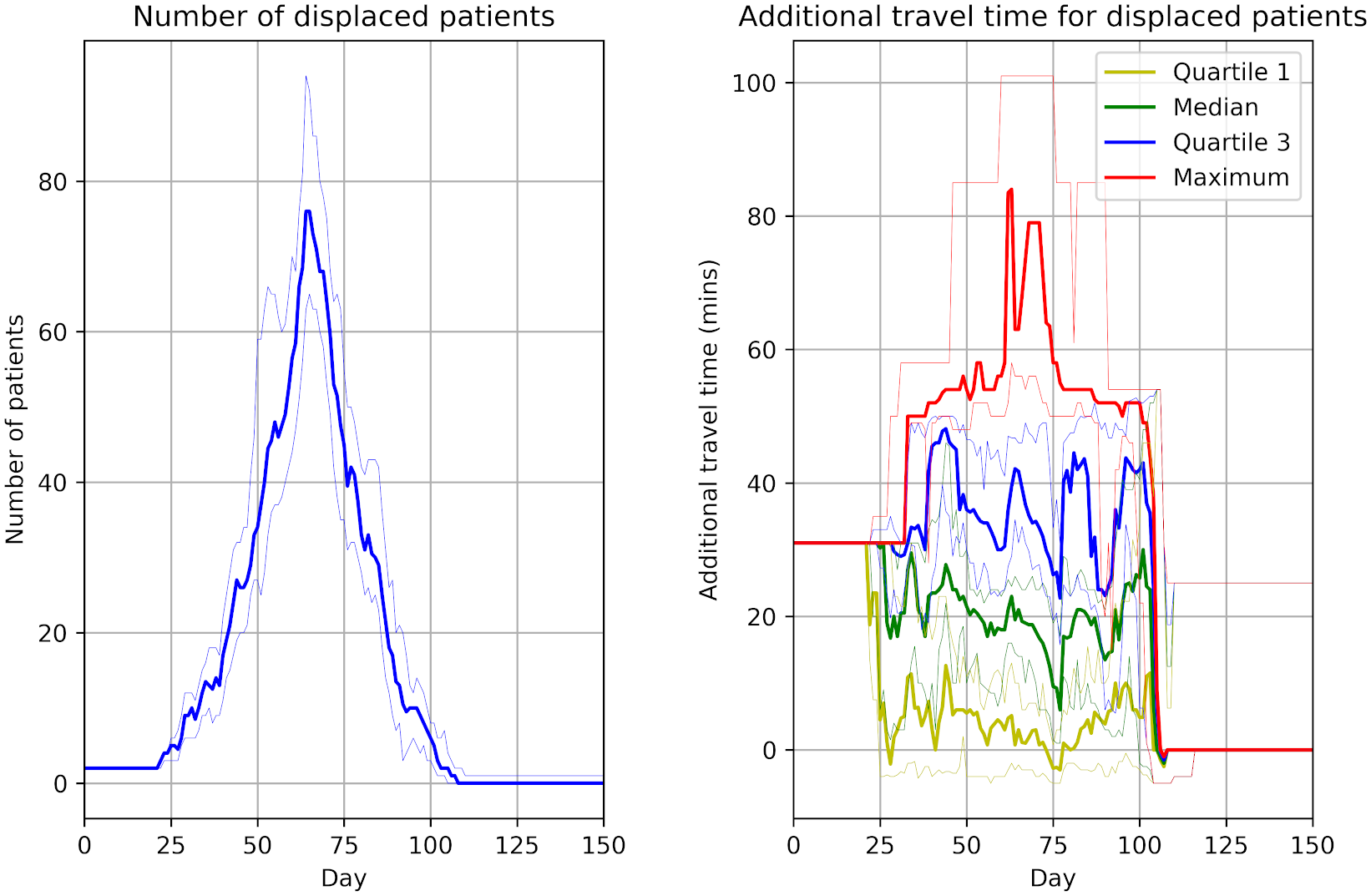
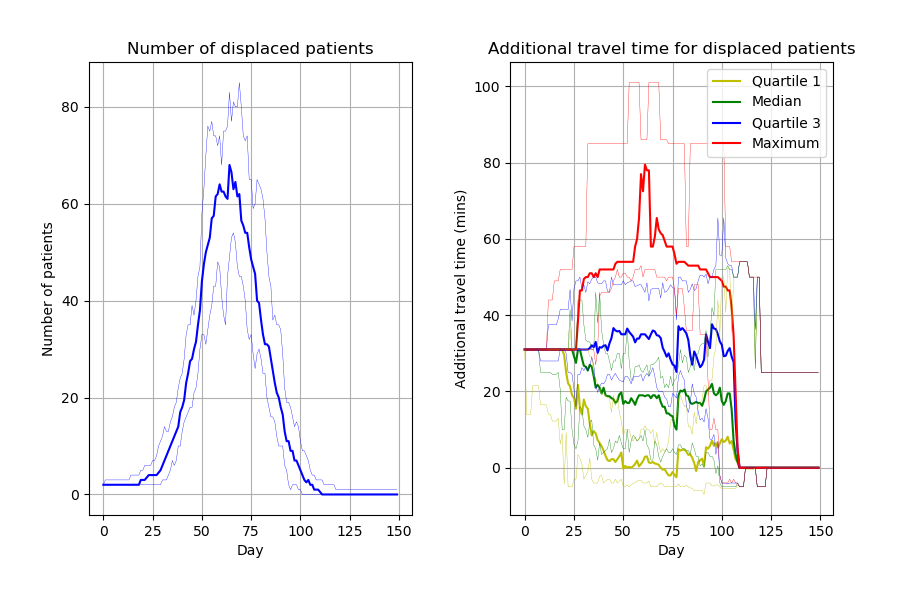
Successfully reproduced all 3 figures (100%) within scope in 7h 6m (17.8%).
Required troubleshooting:
- Add joblib and remove spyder from environment.yaml
- Modifications to enable control for randomness with individual random number streams
Evaluation against guidelines
Context: The original study repository was evaluated against guidance for sharing of artefacts (best practice audit and STARS) and against criteria from journal badges relating to how open and reproducible the model is. The original study article and supplementary materials (excluding code) were evaluated against reporting guidelines for DES models: STRESS-DES, and guidelines adapted from ISPOR-SDM.