| Scenario | Testing interval | Costs per patient | QALYs per patient | ICER | INMB (ranking) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | S0: No case detection | NaN | $2150 | 12.545 | NaN | NaN |
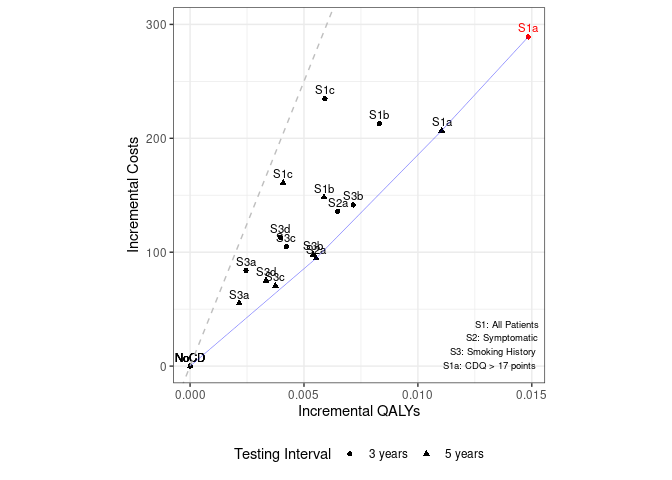
| 1 | (S1a) CDQ ≥ 17 points | 3 years | $2439 | 12.560 | 19472.0 | 453(1) |
| 2 | (S1a) CDQ ≥ 17 points | 5 years | $2357 | 12.557 | 18717.0 | 346(2) |
| 3 | (S1b) Screening spirometry | 3 years | $2363 | 12.554 | 25644.0 | 202(4) |
| 4 | (S1b) Screening spirometry | 5 years | $2298 | 12.551 | 25236.0 | 146(8) |
| 5 | (S1c) CDQ + screening spirometry | 3 years | $2385 | 12.551 | 39678.0 | 61(13) |
| 6 | (S1c) CDQ + screening spirometry | 5 years | $2311 | 12.550 | 39400.0 | 43(15) |
| 7 | (S2a) Screening spirometry | 3 years | $2286 | 12.552 | 21002.0 | 188(5) |
| 8 | (S2a) Screening spirometry | 5 years | $2245 | 12.551 | 17109.0 | 182(6) |
| 9 | (S3a) CDQ ≥ 19.5 points | 3 years | $2234 | 12.548 | 34157.0 | 39(16) |
| 10 | (S3a) CDQ ≥ 19.5 points | 5 years | $2205 | 12.548 | 25648.0 | 52(14) |
| 11 | (S3b) CDQ ≥ 16.5 points | 3 years | $2291 | 12.553 | 19763.0 | 216(3) |
| 12 | (S3b) CDQ ≥ 16.5 points | 5 years | $2248 | 12.551 | 18093.0 | 173(7) |
| 13 | (S3c) Screening spirometry | 3 years | $2255 | 12.550 | 24778.0 | 107(10) |
| 14 | (S3c) Screening spirometry | 5 years | $2220 | 12.549 | 18842.0 | 117(9) |
| 15 | (S3d) CDQ + screening spirometry | 3 years | $2263 | 12.549 | 28562.0 | 85(12) |
| 16 | (S3d) CDQ + screening spirometry | 5 years | $2225 | 12.549 | 22545.0 | 91(11) |
Summary report
For computational reproducibility assessment of Johnson et al. 2021
Study
Johnson, K.M., Sadatsafavi, M., Adibi, A., Lynd, L., Harrison, M., Tavakoli, H., Sin, D., Bryan, S. Cost Effectiveness of Case Detection Strategies for the Early Detection of COPD. Applied Health Economics and Health Policy 19, p203-215 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40258-020-00616-2.
This study uses a previously validated discrete-event simulation model, EPIC: Evaluation Platform in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The model is written in C++ with an R interface, using R scripts for execution. The model is adapted to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of 16 COPD case detection strategies in primary care, comparing costs, quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICER), and incremental net monetary benefits (INMB) across scenarios. Sensitivity analyses are also conducted.
Computational reproducibility
Successfully reproduced 4 out of 5 (80%) of items from the scope in 19h 49m (49.5%).
Required troubleshooting:
- Environment - identifying required packages, importing archived packages, and local import of the
epicRpackage - Run time - troubleshooting with lower agent numbers due to long run times
- Output files - saves results to
.csv - Tables and figures - writing code to produce these, which required figuring out:
- Which results tables to use
- Which columns to use
- Which scenarios to use
- How to transform the columns
- How to create features like the efficiency frontier
- Sensitivity analysis - identifying parameters to change and creating scripts
Cannot display original figure as do not have permission for reuse, but can view at Johnson et al. (2021)
Reproduction:
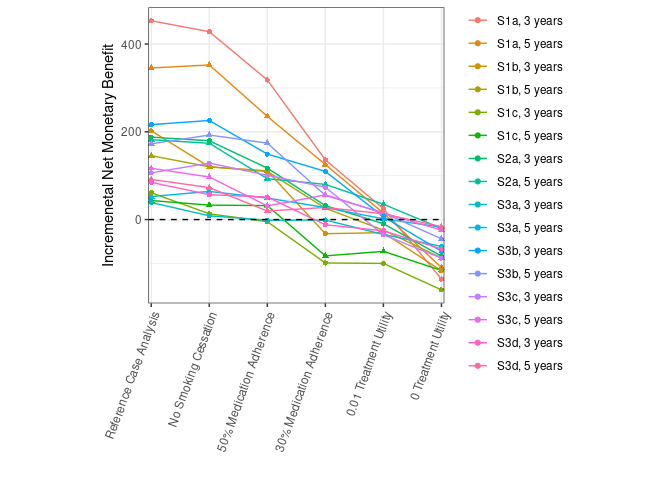
Cannot display original figure as do not have permission for reuse, but can view at Johnson et al. (2021)
Reproduction:
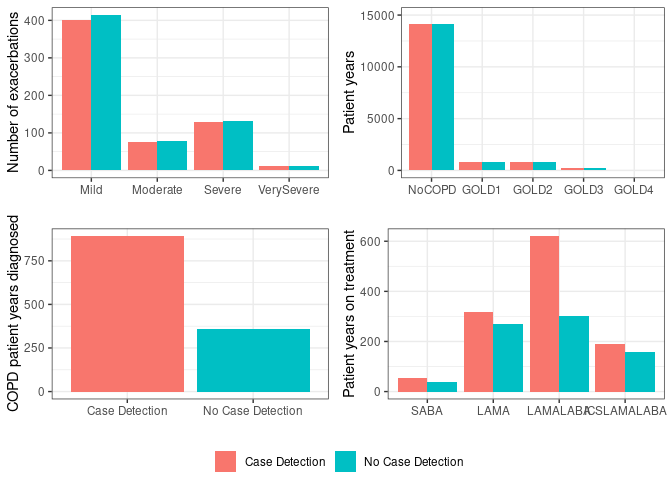
Cannot display original figure as do not have permission for reuse, but can view at Johnson et al. (2021)
Reproduction:
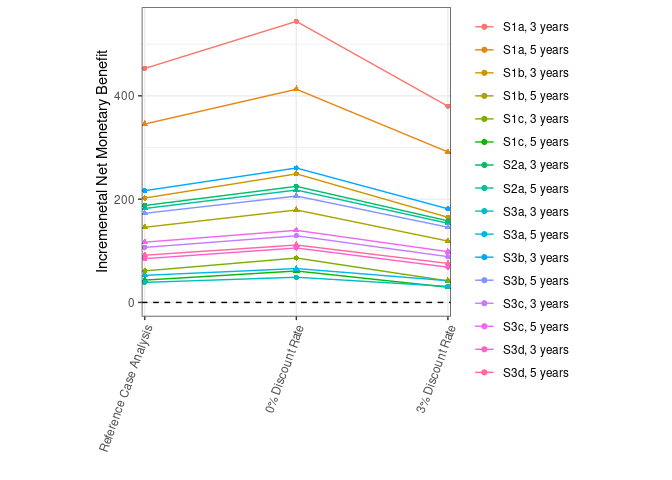
Cannot display original figure as do not have permission for reuse, but can view at Johnson et al. (2021)
Reproduction:
Cannot display original figure as do not have permission for reuse, but can view at Johnson et al. (2021)
Reproduction:
Evaluation against guidelines
Context: The original study repository was evaluated against criteria from journal badges relating to how open and reproducible the model is and against guidance for sharing artefacts from the STARS framework. The original study article and supplementary materials (excluding code) were evaluated against reporting guidelines for DES models: STRESS-DES, and guidelines adapted from ISPOR-SDM.