library(simmer)
library(tibble)
library(ggplot2)
suppressMessages(library(RCurl))Time-dependent arrivals
1. Background
The treatment simulation model has a time-dependent arrival profile for patients. To simulated these arrivals correctly in DES we need to use one of several algorithms. Here we make use of the thinning algorithm.
Thinning is a acceptance-rejection sampling method and is used to generate inter-arrival times from a NSPP.
Motivation: In DES we use thinning as an approach to generate time dependent arrival of patients to a health care service.
1.1 An example NSPP
The table below is adapted from Banks et al (2013) and breaks an arrival process down into 60 minutes intervals.
| t(min) | Mean time between arrivals (min) | Arrival Rate \(\lambda(t)\) (arrivals/min) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 15 | 1/15 |
| 60 | 12 | 1/12 |
| 120 | 7 | 1/7 |
| 180 | 5 | 1/5 |
| 240 | 8 | 1/8 |
| 300 | 10 | 1/10 |
| 360 | 15 | 1/15 |
| 420 | 20 | 1/20 |
| 480 | 20 | 1/20 |
Interpretation: In the table above the fastest arrival rate is 1/5 customers per minute or 5 minutes between patient arrivals.
1.2 The thinning algorithm
A NSPP has arrival rate \(\lambda(t)\) where \(0 \leq t \leq T\)
Here \(i\) is the arrival number and \(\mathcal{T_i}\) is its arrival time.
Let \(\lambda^* = \max_{0 \leq t \leq T}\lambda(t)\) be the maximum of the arrival rate function and set \(t = 0\) and \(i=1\)
Generate \(e\) from the exponential distribution with rate \(\lambda^*\) and let \(t = t + e\) (this is the time of the next entity will arrive)
Generate \(u\) from the \(U(0,1)\) distribution. If \(u \leq \dfrac{\lambda(t)}{\lambda^*}\) then \(\mathcal{T_i} =t\) and \(i = i + 1\)
Go to Step 2.
2. Imports
3. Read in data
Here we read in the example non-stationary data and compute the arrival rate.
NSPP_PATH = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TomMonks/treat-sim-rsimmer/main/data/nspp_example1.csv'
csv_data <- getURL(NSPP_PATH)
arrivals <- read.csv(text=csv_data)
names(arrivals) <- c("period", "mean_iat")
# create arrival rate
arrivals$arrival_rate = 1.0 / arrivals$mean_iat
arrivals period mean_iat arrival_rate
1 0 15 0.06666667
2 60 12 0.08333333
3 120 7 0.14285714
4 180 5 0.20000000
5 240 8 0.12500000
6 300 10 0.10000000
7 360 15 0.06666667
8 420 20 0.05000000
9 480 20 0.05000000ggplot(data=arrivals, aes(x=period, y=mean_iat)) +
geom_bar(stat="identity", fill="steelblue") +
xlab("Time of day (mins)") +
ylab("Mean IAT (min)")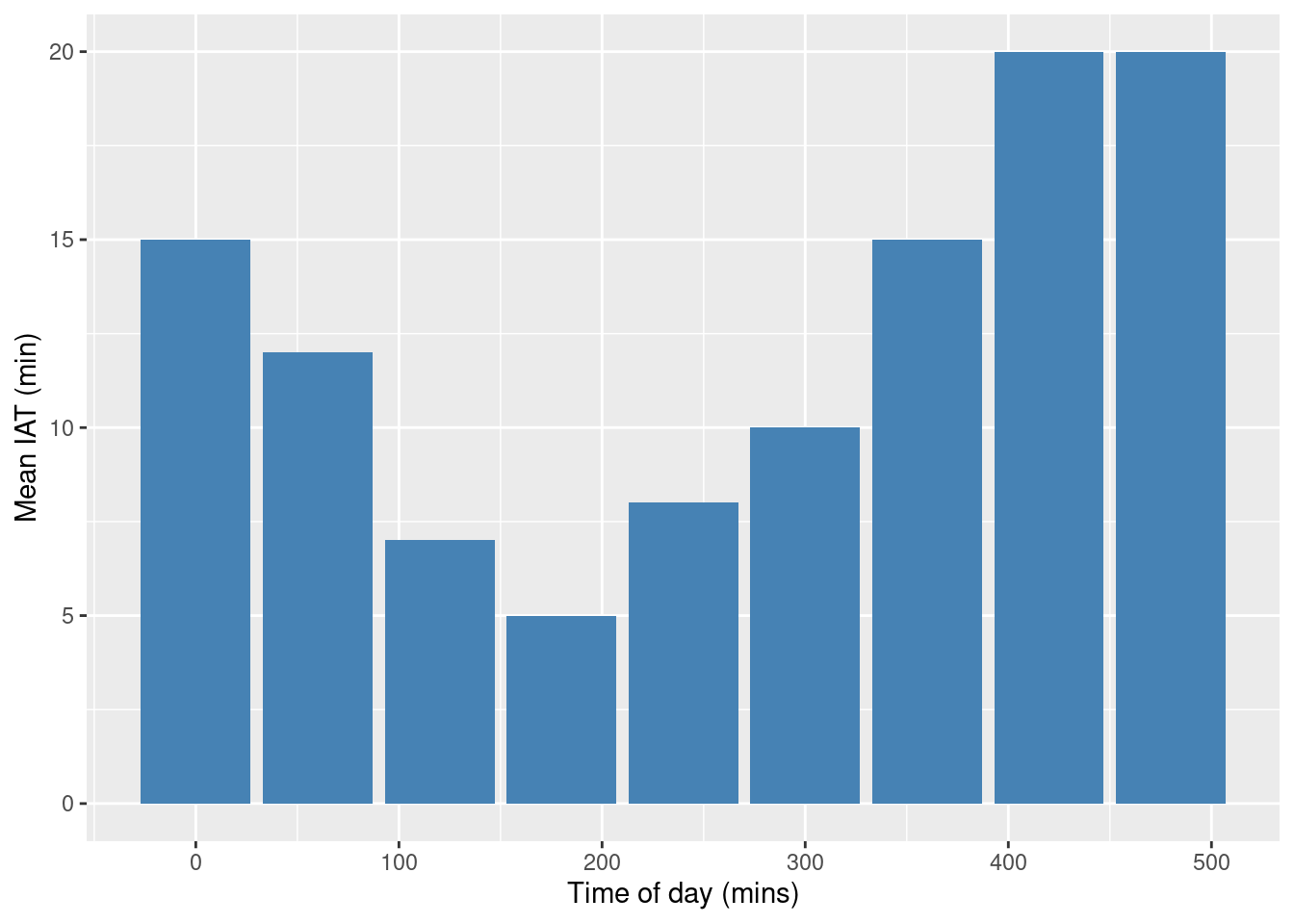
4. Algorithm implementation
4.1 NSPP sampling function
nspp_thinning <- function(simulation_time, data, debug=FALSE){
# calc time interval: assumes intervals are of equal length
interval <- data$period[2] - data$period[1]
# maximum arrival rate (smallest time between arrivals)
lambda_max <- max(data$arrival_rate)
while(TRUE){
# get time bucket (row of dataframe to use)
t <- floor(simulation_time / interval) %% nrow(data) + 1
lambda_t <- data$arrival_rate[t]
# set to a large number so that at least 1 sample is taken
u <- Inf
rejects <- -1
# running total of time until next arrival
inter_arrival_time <- 0.0
# reject proportionate to lambda_t / lambda_max
ratio <- lambda_t / lambda_max
while(u >= ratio){
rejects <- rejects + 1
# sample using max arrival rate
inter_arrival_time <- inter_arrival_time + rexp(1, lambda_max)
u <- runif(1, 0.0, 1.0)
}
if(debug){
print({paste("Time:", simulation_time,
" Rejections:", rejects,
" t:", t,
" lambda_t:", lambda_t,
" IAT:", inter_arrival_time)})
}
return(inter_arrival_time)
}
}4.2 Example usage
The function can be used in the same way as rexp to generate new patients. To illustrate its use we first create a simple patient pathway trajectory that prints out some event and acts as a delay.
patient <- trajectory("patient pathway") %>%
# just a simple delay
log_(function() {paste("Patient arrival")}, level = 1) %>%
timeout(function() rnorm(1, 10.0, 1.0)) %>%
log_(function() {paste("Exit treatment pathway")}, level = 1)We then run the model with a generator that uses the nspp_thinning sampling function. Note that the function accepts the current simulation time now(env) and the dataframe containing the arrivals arrivals.
Important learning point: we need to detach
runfrom the creation of the simulation environment. This will allownow(env)to run correctly. If we ignore this rule and includerunin the creation pipe the same time will be passed to the thinning function and it will under/over sample arrivals. See https://r-simmer.org/articles/simmer-03-trajectories.html
env <- simmer("TreatSim", log_level=0)
env %>%
add_generator("patient", patient,
function() nspp_thinning(now(env), arrivals, debug=TRUE)) %>%
run(until=540.0)[1] "Time: 0 Rejections: 2 t: 1 lambda_t: 0.0666666666666667 IAT: 12.3170700045055"
[1] "Time: 12.3170700045055 Rejections: 2 t: 1 lambda_t: 0.0666666666666667 IAT: 29.8042921362527"
[1] "Time: 42.1213621407582 Rejections: 4 t: 1 lambda_t: 0.0666666666666667 IAT: 44.3244025730205"
[1] "Time: 86.4457647137787 Rejections: 0 t: 2 lambda_t: 0.0833333333333333 IAT: 1.5125033070694"
[1] "Time: 87.9582680208481 Rejections: 1 t: 2 lambda_t: 0.0833333333333333 IAT: 4.80466362067914"
[1] "Time: 92.7629316415272 Rejections: 0 t: 2 lambda_t: 0.0833333333333333 IAT: 2.07653273129836"
[1] "Time: 94.8394643728255 Rejections: 1 t: 2 lambda_t: 0.0833333333333333 IAT: 12.7656335775265"
[1] "Time: 107.605097950352 Rejections: 1 t: 2 lambda_t: 0.0833333333333333 IAT: 6.69238817158571"
[1] "Time: 114.297486121938 Rejections: 3 t: 2 lambda_t: 0.0833333333333333 IAT: 11.4083337817366"
[1] "Time: 125.705819903674 Rejections: 0 t: 3 lambda_t: 0.142857142857143 IAT: 0.232516925316304"
[1] "Time: 125.938336828991 Rejections: 1 t: 3 lambda_t: 0.142857142857143 IAT: 6.2632446431317"
[1] "Time: 132.201581472122 Rejections: 0 t: 3 lambda_t: 0.142857142857143 IAT: 1.50837458437309"
[1] "Time: 133.709956056495 Rejections: 0 t: 3 lambda_t: 0.142857142857143 IAT: 3.85685536989427"
[1] "Time: 137.56681142639 Rejections: 2 t: 3 lambda_t: 0.142857142857143 IAT: 20.6832564180142"
[1] "Time: 158.250067844404 Rejections: 0 t: 3 lambda_t: 0.142857142857143 IAT: 6.35431296636766"
[1] "Time: 164.604380810772 Rejections: 3 t: 3 lambda_t: 0.142857142857143 IAT: 45.955617979437"
[1] "Time: 210.559998790209 Rejections: 0 t: 4 lambda_t: 0.2 IAT: 1.42062998576036"
[1] "Time: 211.980628775969 Rejections: 0 t: 4 lambda_t: 0.2 IAT: 0.458430694988776"
[1] "Time: 212.439059470958 Rejections: 0 t: 4 lambda_t: 0.2 IAT: 5.25860620175904"
[1] "Time: 217.697665672717 Rejections: 0 t: 4 lambda_t: 0.2 IAT: 4.17272278086698"
[1] "Time: 221.870388453584 Rejections: 0 t: 4 lambda_t: 0.2 IAT: 0.229960032738745"
[1] "Time: 222.100348486322 Rejections: 0 t: 4 lambda_t: 0.2 IAT: 0.652627080552088"
[1] "Time: 222.752975566875 Rejections: 0 t: 4 lambda_t: 0.2 IAT: 6.63534692933268"
[1] "Time: 229.388322496207 Rejections: 0 t: 4 lambda_t: 0.2 IAT: 5.01297508811063"
[1] "Time: 234.401297584318 Rejections: 0 t: 4 lambda_t: 0.2 IAT: 2.69523442257196"
[1] "Time: 237.09653200689 Rejections: 0 t: 4 lambda_t: 0.2 IAT: 2.71995460847393"
[1] "Time: 239.816486615364 Rejections: 0 t: 4 lambda_t: 0.2 IAT: 5.35320844014591"
[1] "Time: 245.16969505551 Rejections: 1 t: 5 lambda_t: 0.125 IAT: 6.91582239444783"
[1] "Time: 252.085517449958 Rejections: 0 t: 5 lambda_t: 0.125 IAT: 6.39692617551118"
[1] "Time: 258.482443625469 Rejections: 1 t: 5 lambda_t: 0.125 IAT: 33.31127954999"
[1] "Time: 291.793723175459 Rejections: 0 t: 5 lambda_t: 0.125 IAT: 6.32686956764615"
[1] "Time: 298.120592743105 Rejections: 0 t: 5 lambda_t: 0.125 IAT: 0.6473648018442"
[1] "Time: 298.767957544949 Rejections: 0 t: 5 lambda_t: 0.125 IAT: 0.562435596448654"
[1] "Time: 299.330393141398 Rejections: 0 t: 5 lambda_t: 0.125 IAT: 14.3972218773308"
[1] "Time: 313.727615018728 Rejections: 0 t: 6 lambda_t: 0.1 IAT: 4.03505245840212"
[1] "Time: 317.762667477131 Rejections: 0 t: 6 lambda_t: 0.1 IAT: 12.9321964642472"
[1] "Time: 330.694863941378 Rejections: 0 t: 6 lambda_t: 0.1 IAT: 8.29896487253618"
[1] "Time: 338.993828813914 Rejections: 1 t: 6 lambda_t: 0.1 IAT: 4.86410341841185"
[1] "Time: 343.857932232326 Rejections: 1 t: 6 lambda_t: 0.1 IAT: 8.14657132614103"
[1] "Time: 352.004503558467 Rejections: 1 t: 6 lambda_t: 0.1 IAT: 5.96838979960835"
[1] "Time: 357.972893358075 Rejections: 0 t: 6 lambda_t: 0.1 IAT: 0.566974185257226"
[1] "Time: 358.539867543332 Rejections: 2 t: 6 lambda_t: 0.1 IAT: 17.9213087428416"
[1] "Time: 376.461176286174 Rejections: 2 t: 7 lambda_t: 0.0666666666666667 IAT: 7.19756458909887"
[1] "Time: 383.658740875273 Rejections: 7 t: 7 lambda_t: 0.0666666666666667 IAT: 28.6240846114835"
[1] "Time: 412.282825486756 Rejections: 7 t: 7 lambda_t: 0.0666666666666667 IAT: 37.641882830785"
[1] "Time: 449.924708317541 Rejections: 0 t: 8 lambda_t: 0.05 IAT: 6.7952759422124"
[1] "Time: 456.719984259754 Rejections: 1 t: 8 lambda_t: 0.05 IAT: 6.45498812368717"
[1] "Time: 463.174972383441 Rejections: 2 t: 8 lambda_t: 0.05 IAT: 12.2225909600384"
[1] "Time: 475.397563343479 Rejections: 0 t: 8 lambda_t: 0.05 IAT: 11.025298134725"
[1] "Time: 486.422861478204 Rejections: 5 t: 9 lambda_t: 0.05 IAT: 14.8031513880246"
[1] "Time: 501.226012866229 Rejections: 0 t: 9 lambda_t: 0.05 IAT: 7.47590314554882"
[1] "Time: 508.701916011778 Rejections: 5 t: 9 lambda_t: 0.05 IAT: 36.0732168012259"simmer environment: TreatSim | now: 540 | next: 544.775132813004
{ Monitor: in memory }
{ Source: patient | monitored: 1 | n_generated: 52 }5. Validation
The total number of arrivals in 540 minutes
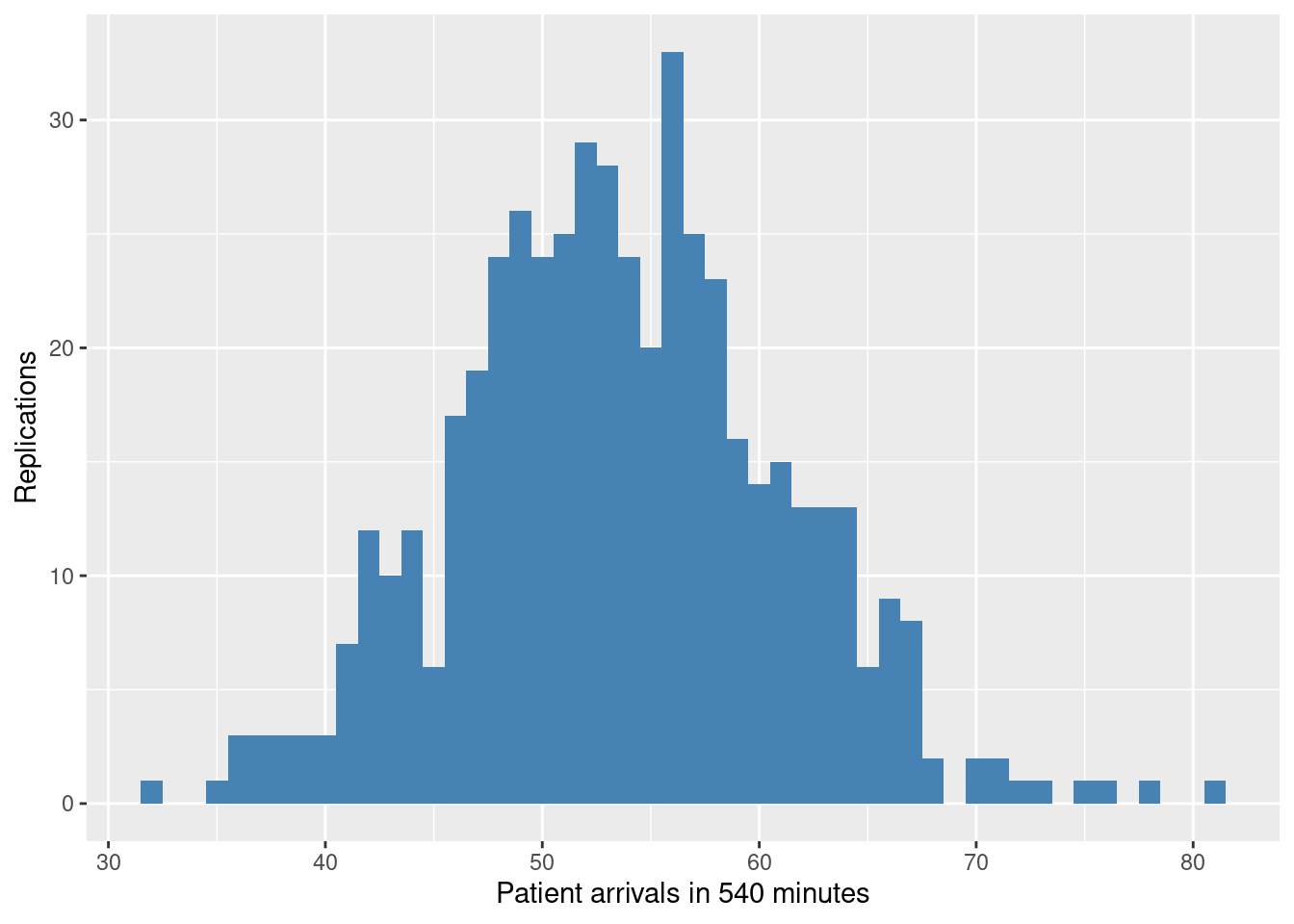
Here we will repeat the same 10,000 times and then explore the distribution of the number of arrivals. If all has gone to plan this should be a Poisson distribution with mean ~53.
# expected arrivals from data.
round(sum(arrivals$arrival_rate * 60), 2)[1] 53.07We can use the simmer function get_n_generated to return the number of patients generated.
arrivals_by_replication <- function(envs){
results <- vector()
for(env in envs){
results <- c(results, get_n_generated(env, "patient"))
}
return(data.frame(results))
}single_run <- function(env, rep_number, run_length, debug_arrivals=FALSE){
env %>%
add_generator("patient", patient,
function() nspp_thinning(now(env), arrivals, debug=debug_arrivals)) %>%
run(until=540.0)
return(env)
}RUN_LENGTH <- 540.0
N_REPS <- 500
SEED <- 42
set.seed(SEED)
patient <- trajectory("patient pathway") %>%
# just a simple delay
log_(function() {paste("Exit treatment pathway")}, level = 1)
# note unlike in simmer documentation we use a traditional for loop
# instead of lapply. This allows us to separeate env creation
# from run and preserve the environment interaction between NSPP
# and current sim time.
envs = vector()
for(rep in 1:N_REPS){
env <- simmer("TreatSim", log_level=0)
single_run(env, i, RUN_LENGTH)
envs <- c(envs, env)
}
# # get the number of arrivals generated
results <- arrivals_by_replication(envs)
# show mean number of arrivals. Should be close to 53
mean(results$results)[1] 53.552ggplot(results, aes(x=results)) +
geom_histogram(binwidth=1, fill="steelblue") +
xlab("Patient arrivals in 540 minutes") +
ylab("Replications")